RNA Transcription
Prerequisite Material
INTRODUCTION
Recall Objectives: Each first year medical student is expected to be able to:
- List the basic concepts about RNA biosynthesis
- Define the relationship between the coding DNA sequence, the transcribed mRNA sequence and the translated protein sequence
- Know the essential properties of RNA polymerases
Reference: Textbook of Biochemistry with Clinical Correlations, Devlin, 7th ediction, Chapters 5 and 8
Basic Concepts of RNA Biosynthesis (Transcription)
- All eukaryotic cellular RNAs are synthesized using a DNA template and a DNA-dependent RNA polymerase.
- Synthesis proceeds in a 5' to 3' direction.
- The three major types of cellular RNAs (ribosomal, transfer and messenger) are first synthesized as large molecular weight precursors which are processed specifically to produce the final mature RNA species.
- The initiation step of transcription is especially highly regulated.
RNA Polymerases
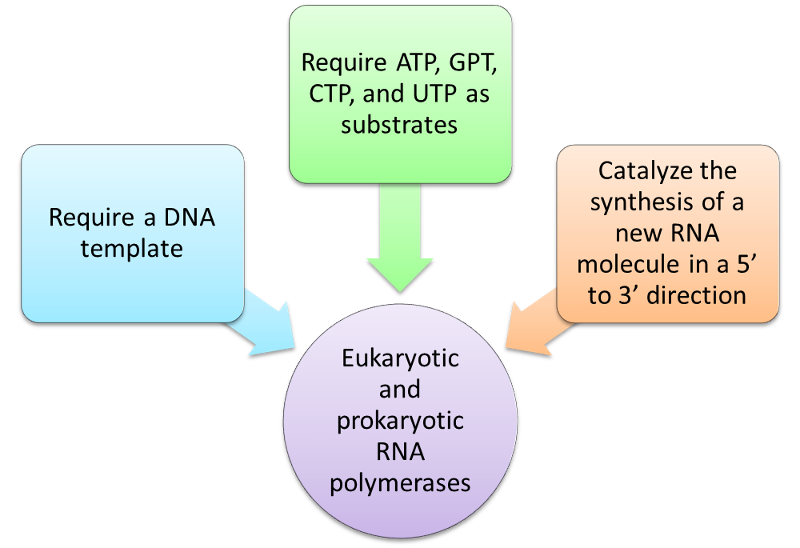
In prokaryotes, a single type of enzyme is responsible for the synthesis of all three types of cellular RNA species
In eukaryotes, four types of RNA polylmerase, each responsible for synthesis of a specific cellular RNA species. Abbreviations are: RNA polymerase I, pol I; RNA polymerase II, pol II; RNA polymerase III, pol III.

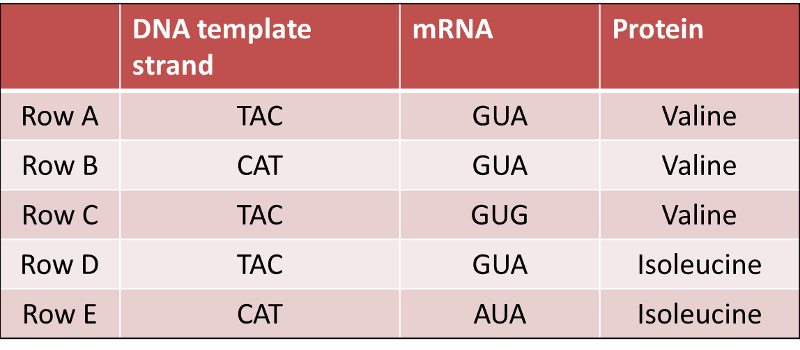
Quick Check


References and Credits
Images
All images created with resources in the public domain on behalf of the Undergraduate Medical Education office, School of Medicine, University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio.





